Exploring New and Expansive Hyperloop Technologies
HYPED’s research team is one of the three main pillars of the society and pushes forward into areas the technical team have yet to explore. Every year, the research team delves into the many aspects of Hyperloop technology with intent to improve its implementation and bring it a step closer to reality.
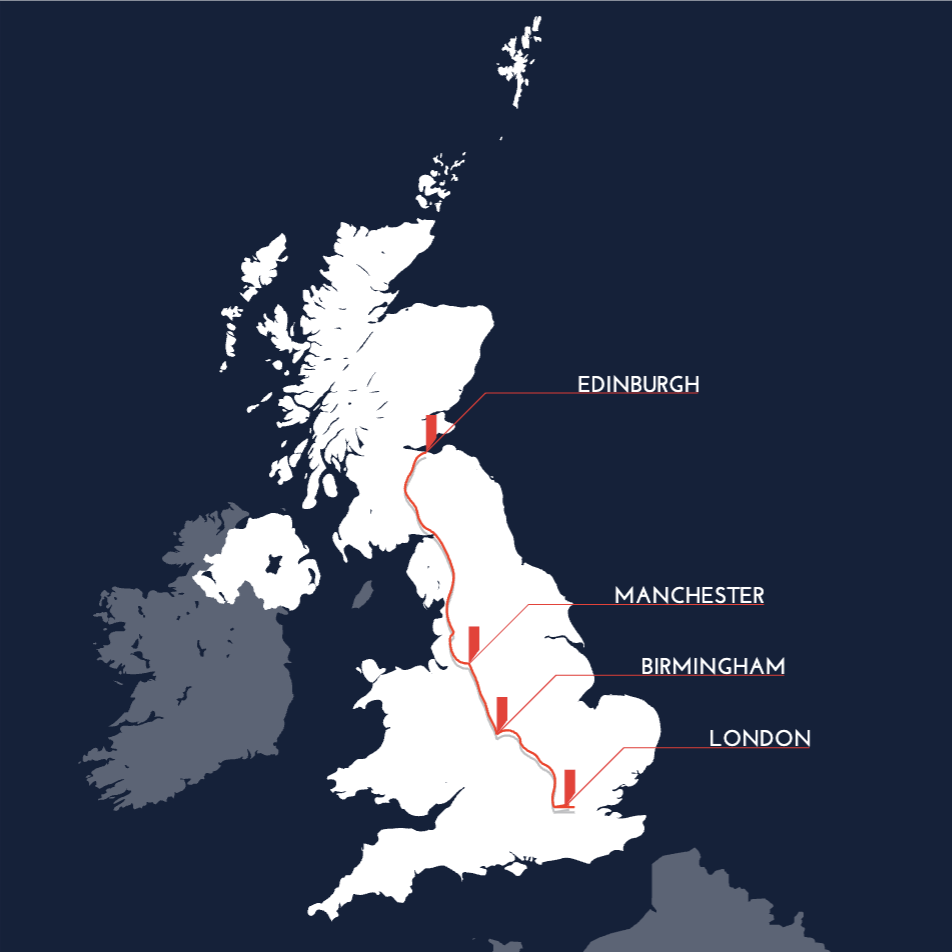
HYPED are winners of the Virgin Hyperloop One Global Challenge in 2017, having proposed a route connecting Edinburgh to London in 50 minutes. Our proposal discussed the feasibility of Hyperloop in the UK, highlighting the social, economic and environmental impacts. Out of 2600 entries, HYPED is one of ten winners across the globe and the only student team to have won the Global Challenge.
Since 2021, we have been publishing and presenting our paper at European Hyperloop Week (EHW), where it is shared and competes with publications from other Hyperloop teams. HYPED has proven to provide great contributions in the research side of the Hyperloop community as we were selected as the top 4 finalists for the full-scale research category in EHW 2023.
- The UK Spine; A Regenerative Project for the United Kingdom<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2017","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null}, {"title": "2019","description": "
-
2017
The UK Spine; A Regenerative Project for the United Kingdom
-
2019
Observing The Complexity Of A Hyperloop: Beyond The Sphere Of A Technical Marvel
-
2021
Investigation into the feasibility of introducing Hyperloop to the UK Contents
-
2022
Feasibility Study of Suspension and Levitation Systems for a Hyperloop System
-
2023
Integration and Performance Study of Vacuum Pumps and Airlocks in a Hyperloop System
Observing The Complexity Of A Hyperloop: Beyond The Sphere Of A Technical Marvel<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2019","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null}, {"title": "2021","description": "
Investigation into the feasibility of introducing Hyperloop to the UK Contents<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2021","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null}, {"title": "2022","description": "
Feasibility Study of Suspension and Levitation Systems for a Hyperloop System<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2022","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null}, {"title": "2023","description": "
Integration and Performance Study of Vacuum Pumps and Airlocks in a Hyperloop System<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2023","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null} ],"styles": {"imageFocalPoint": {"x": 0.5,"y": 0.5},"imageOverlayOpacity": 0.3,"sectionTheme": "white-bold","imageEffect": "none","backgroundMode": "image","backgroundColor": "white","backgroundImage": null},"video": {"filter": 1,"videoFallbackContentItem": null,"nativeVideoContentItem": null,"videoSourceProvider": "none"},"backgroundImageFocalPoint": null,"backgroundImageId": null,"options": {"maxColumns": 5,"isCardEnabled": true,"isMediaEnabled": false,"isTitleEnabled": true,"isBodyEnabled": true,"isButtonEnabled": true,"mediaAspectRatio": "circle","layoutWidth": "inset","mediaWidth": {"value": 100,"unit": "%"},"mediaAlignment": "center","contentWidth": {"value": 100,"unit": "%"},"titleAlignment": "center","bodyAlignment": "center","buttonAlignment": "center","titlePlacement": "center","bodyPlacement": "center","buttonPlacement": "center","cardVerticalAlignment": "stretch","contentOrder": "media-first","verticalPaddingTop": {"value": 6.6,"unit": "vmax"},"verticalPaddingBottom": {"value": 6.6,"unit": "vmax"},"spaceBetweenColumns": {"value": 20,"unit": "px"},"spaceBetweenRows": {"value": 20,"unit": "px"},"spaceBetweenContentAndMedia": {"value": 10,"unit": "%"},"spaceBelowTitle": {"value": 10,"unit": "%"},"spaceBelowBody": {"value": 10,"unit": "%"},"cardPaddingTop": {"value": 10,"unit": "%"},"cardPaddingRight": {"value": 10,"unit": "%"},"cardPaddingBottom": {"value": 10,"unit": "%"},"cardPaddingLeft": {"value": 10,"unit": "%"},"titleFontSize": "heading-2","bodyFontSize": "paragraph-2","buttonFontSize": "button-medium","customOptions": {"customTitleFontSize": {"value": 1.2,"unit": "rem"},"customBodyFontSize": {"value": 0.9,"unit": "rem"},"customButtonFontSize": {"value": 0.8,"unit": "rem"}}},"layout": "simple","isSectionTitleEnabled": false,"sectionTitle": "
<\/p>","spaceBelowSectionTitle": {"value": 120,"unit": "px"},"sectionTitleAlignment": "center","isSectionButtonEnabled": false,"sectionButton": {"buttonText": "Make It","buttonLink": "#","buttonNewWindow": false},"sectionButtonSize": "medium","sectionButtonAlignment": "center","spaceAboveSectionButton": {"value": 120,"unit": "px"}}” data-media-alignment=”center” data-title-alignment=”center” data-body-alignment=”center” data-button-alignment=”center” data-title-placement=”center” data-body-placement=”center” data-button-placement=”center” data-layout-width=”inset” data-title-font-unit=”rem” data-description-font-unit=”rem” data-button-font-unit=”rem” data-space-between-rows=”20px” data-space-between-columns=”20px” data-vertical-padding-top-value=”6.6″ data-vertical-padding-bottom-value=”6.6″ data-vertical-padding-top-unit=”vmax” data-vertical-padding-bottom-unit=”vmax”>
2017 – The UK Spine; A Regenerative Project for the United Kingdom
Historically, the United Kingdom has been at the forefront of technological innovation in transportation, from pioneering railways to the world’s first underground system. Hyperloop technology offers promise in bridging economic disparities across Britain. Past transport advancements, like the canal system, fuelled industrial growth and reduced inequalities. Moreover, new trading opportunities spread wealth to communities in proximity to these routes and promoted growth in the local economies.
However, recent reliance on strained conventional rail and air networks has faced consequences such as provoking passenger distress and a loss of competitive advantage.. The proposed UK Spine, a Hyperloop route going through Edinburgh – Manchester – Birmingham – London, aims to bolster sustainability pillars – economic, social, and environmental, by revitalising transport infrastructure. Amid challenges like post-Brexit uncertainties, the government plans to mitigate risks through increased investment in innovative technology research and skill development to drive economic growth and address social inequalities.
2019 – Observing The Complexity Of A Hyperloop: Beyond The Sphere Of A Technical Marvel
Large-scale infrastructure projects, such as the Channel Tunnel, provide extensive benefits, simultaneously pose significant challenges, including disruptions and cost overruns. The Hyperloop, a novel technology, likely anticipates similar challenges that demand innovative solutions. Issues such as project cost and sustainability are prominent, with cost-effectiveness essential for consumers to willingly switch away from traditional transport methods.
Additionally, the potential for cargo transport remains unexplored. Overall, integrating Hyperloop into an ageing public transport system necessitates addressing safety and reliability concerns. Understanding these complexities is important for implementing the technology effectively, ensuring it provides secure and efficient mobility for both people and freight.
2021 – Investigation into the feasibility of introducing Hyperloop to the UK Contents
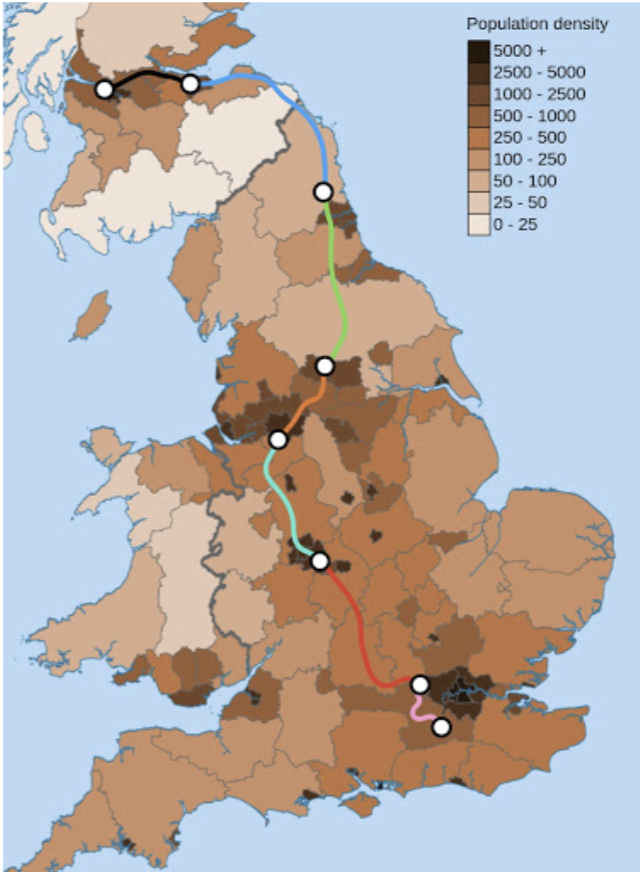
This study on Hyperloop integration into the existing UK transportation network is divided into three sections: Route Planning and Socioeconomic Effects, Cost Estimates and Funding, and Comparison with Other Transport Modes. We aim not to provide a one-and-done solution but rather a series of suggestions that offer the flexibility required when introducing a new mode of transportation, which can be complex. It addresses various Hyperloop designs and routes, considering the benefits and drawbacks of each. Detailed analyses also cover route specifics, demand, cost estimation, and funding options.
Finally, a comparison with existing transport modes in terms of cost, environmental impact, speed, and safety will also be done, recognising the fact that data on Hyperloop relies heavily on estimation and design parameters. Despite challenges, this study emphasises Hyperloop’s potential as a fast, environmentally friendly option, warranting further exploration and effort.
2022 – Feasibility Study of Suspension and Levitation Systems for a Hyperloop System
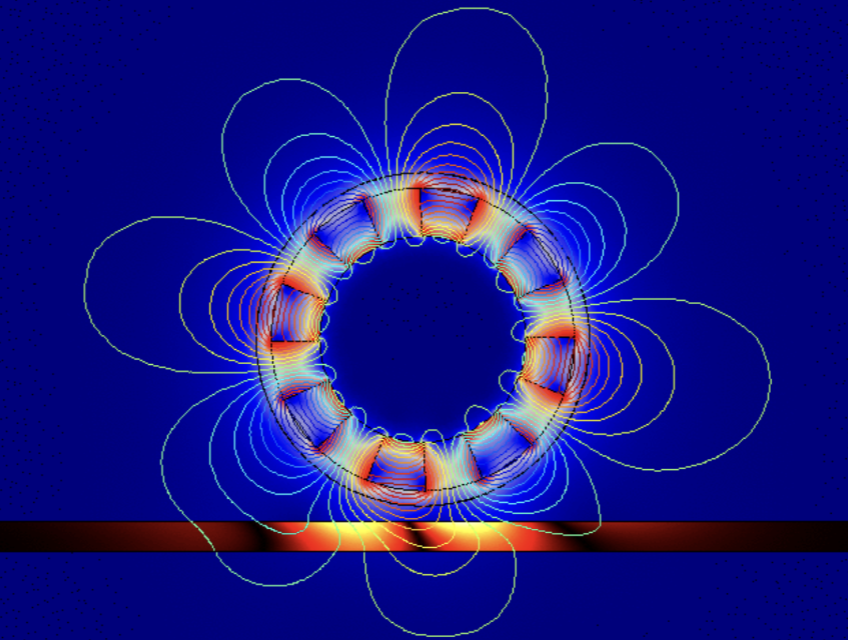
This paper explores the feasibility of four suspension/levitation systems for Hyperloop: wheel-on-rail suspension (WRS), electrodynamic suspension (EDS), electromagnetic suspension (EMS), and electrodynamic wheels (EDW). Each system is analysed in terms of its different technologies, costs, and commercialization potential. While EDW is seen as potentially the cheapest maglev option, it lacks the relevant implementation data needed to compare with the other potential systems. EMS offers dynamic but unstable force, contrasting with EDS’s stability, however, EDS requires a minimum speed for lift while EMS does not. EDW provides lift and thrust at all speeds but possesses a complex configuration. WRS, despite not eliminating wheel-on-track friction, is highly commercialised.
In the end, a conclusive comparison could not be done as there was insufficient data. However, this paper highlights the fact that the limitations of some systems were overcome by others. Due to a lack of information on certain systems, further research will be necessary for a more definitive assessment.
2023 – Integration and Performance Study of Vacuum Pumps and Airlocks in a Hyperloop System
This study examines the optimisation of vacuum pumps and airlocks performance for an efficient Hyperloop system. Various pump technologies like root, rotary vane, and liquid ring pumps are evaluated for their suitability and efficiency in achieving and maintaining the required vacuum levels to maintain a near-vacuum environment in a Hyperloop tube. Furthermore, multiple leakage sources that would be detrimental during implementation have also been studied, resulting in corresponding solutions suggested to mitigate these leakages. Additionally, different airlock systems are analysed based on spatial requirements, safety features, and maintenance.
This paper aims to contribute valuable insights for advancing vacuum pump and airlock technologies in Hyperloop systems, enhancing reliability, and reshaping transportation. By understanding the diverse pump technologies and airlock systems, the engineering of reliable Hyperloop systems are made possible, reshaping the future of transportation.
2024 –
Blank for now
Exploring New and Expansive Hyperloop Technologies
-
HYPED’s research team is one of the three main pillars of the society and pushes forward into areas the technical team have yet to explore. Every year, the research team delves into the many aspects of Hyperloop technology with intent to improve its implementation and bring it a step closer to reality.
HYPED are winners of the Virgin Hyperloop One Global Challenge in 2017, having proposed a route connecting Edinburgh to London in 50 minutes. Our proposal discussed the feasibility of Hyperloop in the UK, highlighting the social, economic and environmental impacts. Out of 2600 entries, HYPED is one of ten winners across the globe and the only student team to have won the Global Challenge.
Since 2021, we have been publishing and presenting our paper at European Hyperloop Week (EHW), where it is shared and competes with publications from other Hyperloop teams. HYPED has proven to provide great contributions in the research side of the Hyperloop community as we were selected as the top 4 finalists for the full-scale research category in EHW 2023.
Observing The Complexity Of A Hyperloop: Beyond The Sphere Of A Technical Marvel<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2019mobile","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null}, {"title": "2021","description": "
Investigation into the feasibility of introducing Hyperloop to the UK Contents <\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2021mobile","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null}, {"title": "2022","description": "
Feasibility Study of Suspension and Levitation Systems for a Hyperloop System<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2022mobile","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null}, {"title": "2023","description": "
Integration and Performance Study of Vacuum Pumps and Airlocks in a Hyperloop System<\/p>","button": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "https://hyp-ed.com/research-2/#2023mobile","buttonNewWindow": false},"image": null} ],"styles": {"imageFocalPoint": {"x": 0.5,"y": 0.5},"imageOverlayOpacity": 0.3,"sectionTheme": "light","imageEffect": "none","backgroundMode": "image","backgroundColor": "white","backgroundImage": null},"video": {"filter": 1,"videoFallbackContentItem": null,"nativeVideoContentItem": null,"videoSourceProvider": "none"},"backgroundImageFocalPoint": null,"backgroundImageId": null,"options": {"maxColumns": 3,"isCardEnabled": false,"isMediaEnabled": true,"isTitleEnabled": true,"isBodyEnabled": true,"isButtonEnabled": true,"isShowAdjacentSlides": true,"isInfiniteEnabled": true,"isAutoplayEnabled": false,"slideDurationMs": 1000,"mediaAspectRatio": "4:3","layoutWidth": "inset","mediaWidth": {"value": 100,"unit": "%"},"mediaAlignment": "left","contentWidth": {"value": 75,"unit": "%"},"titleAlignment": "center","bodyAlignment": "center","buttonAlignment": "center","titlePlacement": "center","bodyPlacement": "center","buttonPlacement": "center","cardVerticalAlignment": "middle","contentOrder": "media-first","titleFontSize": "heading-2","bodyFontSize": "paragraph-2","buttonFontSize": "button-medium","customOptions": {"customTitleFontSize": {"value": 2.2,"unit": "rem"},"customBodyFontSize": {"value": 1,"unit": "rem"},"customButtonFontSize": {"value": 0.8,"unit": "rem"}},"verticalPaddingTop": {"value": 6.6,"unit": "vmax"},"verticalPaddingBottom": {"value": 6.6,"unit": "vmax"},"spaceBetweenSlides": {"value": 60,"unit": "px"},"spaceBetweenContentAndMedia": {"value": 7,"unit": "%"},"spaceBelowTitle": {"value": 7,"unit": "%"},"spaceBelowBody": {"value": 7,"unit": "%"},"cardPaddingTop": {"value": 20,"unit": "px"},"cardPaddingRight": {"value": 20,"unit": "px"},"cardPaddingBottom": {"value": 20,"unit": "px"},"cardPaddingLeft": {"value": 20,"unit": "px"},"navigationOffset": {"value": 5,"unit": "vw"},"navigationControls": "arrows","navigationPlacement": "center","navigationAlignment": "center","spaceAboveNavigation": {"value": 30,"unit": "px"},"progressIndicators": "bars"},"layout": "carousel","isSectionTitleEnabled": false,"sectionTitle": "
<\/p>","spaceBelowSectionTitle": {"value": 40,"unit": "px"},"sectionTitleAlignment": "center","isSectionButtonEnabled": false,"sectionButton": {"buttonText": "Jump to year","buttonLink": "","buttonNewWindow": false},"sectionButtonSize": "small","sectionButtonAlignment": "center","spaceAboveSectionButton": {"value": 23,"unit": "px"}}” data-media-alignment=”left” data-title-alignment=”center” data-body-alignment=”center” data-button-alignment=”center” data-title-placement=”center” data-body-placement=”center” data-button-placement=”center” data-layout-width=”inset” data-title-font-unit=”rem” data-description-font-unit=”rem” data-button-font-unit=”rem” data-is-media-enabled=”true” data-is-card-enabled=”false” data-media-width-value=”100″ data-media-width-unit=”%” data-content-order=”media-first” data-space-between-columns=”” data-vertical-padding-top-value=”6.6″ data-vertical-padding-bottom-value=”6.6″ data-vertical-padding-top-unit=”vmax” data-vertical-padding-bottom-unit=”vmax”>
2017 – The UK Spine; A Regenerative Project for the United Kingdom
-
Historically, the United Kingdom has been at the forefront of technological innovation in transportation, from pioneering railways to the world’s first underground system. Hyperloop technology offers promise in bridging economic disparities across Britain. Past transport advancements, like the canal system, fueled industrial growth and reduced inequalities. Moreover, new trading opportunities spread wealth to communities in proximity to these routes and promoted growth in the local economies.
However, recent reliance on strained conventional rail and air networks has faced consequences such as provoking passenger distress and a loss of competitive advantage.. The proposed UK Spine, a Hyperloop route going through Edinburgh – Manchester – Birmingham – London, aims to bolster sustainability pillars – economic, social, and environmental, by revitalising transport infrastructure. Amid challenges like post-Brexit uncertainties, the government plans to mitigate risks through increased investment in innovative technology research and skill development to drive economic growth and address social inequalities.
2019 – Observing The Complexity Of A Hyperloop: Beyond The Sphere Of A Technical Marvel
-
Large-scale infrastructure projects, such as the Channel Tunnel, provide extensive benefits, simultaneously pose significant challenges, including disruptions and cost overruns. The Hyperloop, a novel technology, likely anticipates similar challenges that demand innovative solutions. Issues such as project cost and sustainability are prominent, with cost-effectiveness essential for consumers to willingly switch away from traditional transport methods.
Additionally, the potential for cargo transport remains unexplored. Overall, integrating Hyperloop into an ageing public transport system necessitates addressing safety and reliability concerns. Understanding these complexities is important for implementing the technology effectively, ensuring it provides secure and efficient mobility for both people and freight.
2021 – Investigation into the feasibility of introducing Hyperloop to the UK Contents
-
This study on Hyperloop integration into the existing UK transportation network is divided into three sections: Route Planning and Socioeconomic Effects, Cost Estimates and Funding, and Comparison with Other Transport Modes. We aim not to provide a one-and-done solution but rather a series of suggestions that offer the flexibility required when introducing a new mode of transportation, which can be complex. It addresses various Hyperloop designs and routes, considering the benefits and drawbacks of each. Detailed analyses also cover route specifics, demand, cost estimation, and funding options.
Finally, a comparison with existing transport modes in terms of cost, environmental impact, speed, and safety will also be done, recognising the fact that data on Hyperloop relies heavily on estimation and design parameters. Despite challenges, this study emphasises Hyperloop’s potential as a fast, environmentally friendly option, warranting further exploration and effort.
2022 – Feasibility Study of Suspension and Levitation Systems for a Hyperloop System
-
This paper explores the feasibility of four suspension/levitation systems for Hyperloop: wheel-on-rail suspension (WRS), electrodynamic suspension (EDS), electromagnetic suspension (EMS), and electrodynamic wheels (EDW). Each system is analysed in terms of its different technologies, costs, and commercialization potential. While EDW is seen as potentially the cheapest maglev option, it lacks the relevant implementation data needed to compare with the other potential systems. EMS offers dynamic but unstable force, contrasting with EDS’s stability, however, EDS requires a minimum speed for lift while EMS does not. EDW provides lift and thrust at all speeds but possesses a complex configuration. WRS, despite not eliminating wheel-on-track friction, is highly commercialised.
In the end, a conclusive comparison could not be done as there was insufficient data. However, this paper highlights the fact that the limitations of some systems were overcome by others. Due to a lack of information on certain systems, further research will be necessary for a more definitive assessment.
2023 – Integration and Performance Study of Vacuum Pumps and Airlocks in a Hyperloop System
-
This study examines the optimisation of vacuum pumps and airlocks performance for an efficient Hyperloop system. Various pump technologies like root, rotary vane, and liquid ring pumps are evaluated for their suitability and efficiency in achieving and maintaining the required vacuum levels to maintain a near-vacuum environment in a Hyperloop tube. Furthermore, multiple leakage sources that would be detrimental during implementation have also been studied, resulting in corresponding solutions suggested to mitigate these leakages. Additionally, different airlock systems are analysed based on spatial requirements, safety features, and maintenance.
This paper aims to contribute valuable insights for advancing vacuum pump and airlock technologies in Hyperloop systems, enhancing reliability, and reshaping transportation. By understanding the diverse pump technologies and airlock systems, the engineering of reliable Hyperloop systems are made possible, reshaping the future of transportation.
2024 –
-
This study on Hyperloop integration into the existing UK transportation network is divided into three sections: Route Planning and Socioeconomic Effects, Cost Estimates and Funding, and Comparison with Other Transport Modes. We aim not to provide a one-and-done solution but rather a series of suggestions that offer the flexibility required when introducing a new mode of transportation, which can be complex. It addresses various Hyperloop designs and routes, considering the benefits and drawbacks of each. Detailed analyses also cover route specifics, demand, cost estimation, and funding options.
Finally, a comparison with existing transport modes in terms of cost, environmental impact, speed, and safety will also be done, recognising the fact that data on Hyperloop relies heavily on estimation and design parameters. Despite challenges, this study emphasises Hyperloop’s potential as a fast, environmentally friendly option, warranting further exploration and effort.
Hello, World!